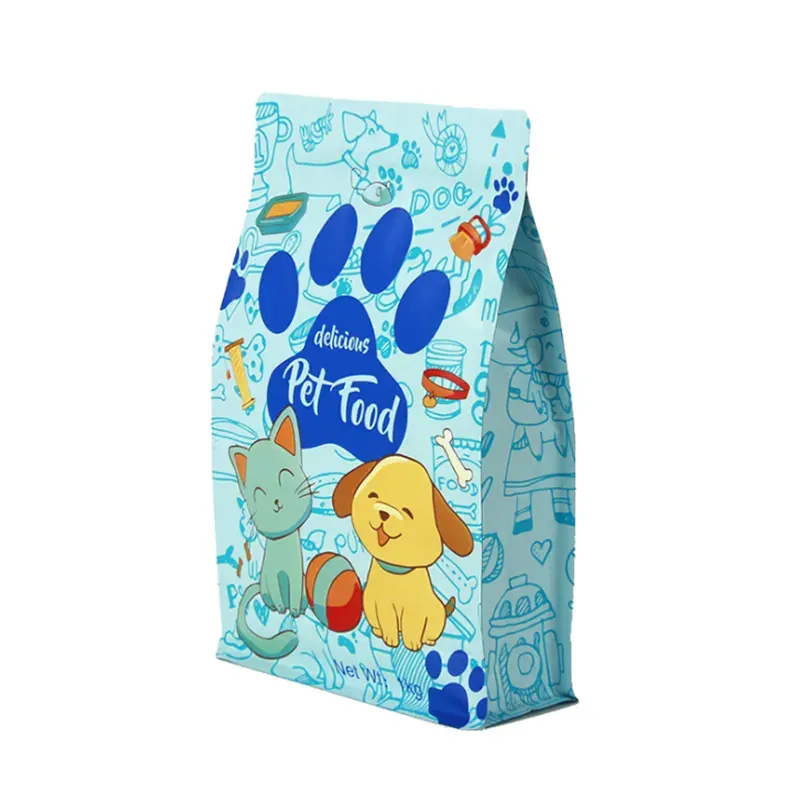
について 平底ポーチ 棚に並べると小さな箱のように見え、積み重ねができ、ブランディングのための大きな印刷領域がある。しかし、棚で存在感を示すことは始まりに過ぎず、真のパフォーマンスは、ジオメトリーのバランスをとる統合デザインにかかっている、 平底袋構造シーリング技術、バリア材料。
この記事は、GQ PACKが配信したものです。 カスタムフレキシブルパッケージングメーカーそのような関係性を説明し、このフォーマットで作業するエンジニア、プロダクトマネージャー、QAチームに実践的な指針を与える。
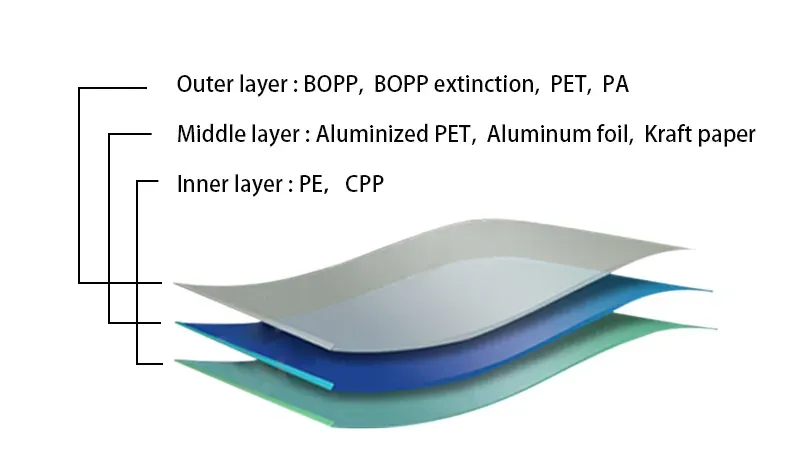
解剖学平底ポーチの構造
最もシンプルなのは 平底ポーチ は、安定したフットプリントを生み出すボックス型またはフラットベースのマルチパネルポーチです。主な構成要素
- フロントパネルとバックパネル - 主要なプリント面。
- 底マチ/箱型ベース - ポーチを立たせるための構造要素。
- サイドパネル(4パネルまたは5パネルデザイン)-プロファイルを形成し、容積効率を高める。
- 上部仕上げ - ヒートシール、ファスナー、または注ぎ口一体型で閉じる。
- シールゾーン - ラミネートとシールが行われる専用の余白。
を理解する 平底袋構造 - パネルの比率、ガセットの形状、シールの配置がどのように相互作用しているかが、予測可能な安定性とシーリング性能の基礎となる。
安定性と構造設計
安定性とは、重心とベースの形状に関するものである。実践的なルールをいくつか紹介しよう:
- ベースの幅と高さの比率: ベースが広いと安定性が増し、ガセットが深いと容積が増えるが、充填時に重心が高くなる可能性がある。製品の密度に合ったベース:高さの比率を目標にする。重い粉体には高さを低くする。
- ガセット形状: 1つ折りのガセットはシンプルで費用対効果が高い。二つ折りやボックス・コーナー・デザインは、ベースがすっきりとした長方形になり、積み重ねもしやすくなります。
- 補強: ラミネートを厚くするか、ベースレイヤーを追加することで、たるみを減らし、充填量の多い製品のスタンドアビリティを向上させることができます。重量のある製品や密度の高い製品には、強化ベースフィルムやラミネートボトムパネルをご検討ください。
- 充填レベルと製品の流れ: 充填不足はパウチを不安定にし、充填過多はシールにストレスを与えます。予想される充填量と粒子の挙動(流動性のあるパウダーとかさばるキブル)に合わせてパウチのサイズを設計する。
人間工学も重要だ。 平底ポーチ 棚から取り出し、注ぎ、消費者が再利用するために再密封するのが簡単でなければならない。
シールシステムと全体
シールはパウチの生命線です。代表的なシールタイプには、フィン/バックシール、ラップシール、ボトムシールなどがあります。ラミネート構造やシール装置によって選択されます。
- シーラントフィルム: 外側のバリア層に適合する内側のシーラントを使用する。一般的なシーラントには、低温または高速シール用に最適化されたPEまたは共押出シーラントブレンドがある。
- シーリング技術: ホット・バー、インパルス、超音波シーリングがすべて使用される。速度、材料の熱プロファイル、部品の形状(スパウトには異なる溶接戦略が必要)に基づいて選択する。
- 一般的な故障モード: コールドシール、層間の汚染、不十分な滞留時間、不適切な圧力。これらはすべて、層間剥離や剥離強度の低下につながる。
- テスト: ピール強度(N/15mm)、破裂/圧力テスト、真空リークテストを実施。シール温度、圧力、速度をインラインでモニターすることにより、ドリフトを防ぎ、再現性を維持します。
良い 平底袋構造 シールゾーンの幅、シーラントの選択、マシンの設定を調整することで、流通や賞味期限までシールを堅牢に保つことができます。
バリア性能:素材構成と測定基準
ポーチの保護機能は、OTR(酸素透過率)、MVTR(水蒸気透過率)、遮光性/紫外線遮断性によって測定される。素材の選択
- ハイバリアラミネート: PET/AL/PE(メタライズドホイル)およびEVOHブレンドは、酸素や湿気に敏感な製品に対して非常に低いOTR/MVTRを提供する。
- モノマテリアルフィルム: モノPEまたはモノPP構造は、リサイクル性が優先される場合に使用されることが多くなっている。中程度のバリアが必要な場合は設計可能だが、高感度製品の場合は二次バリアが必要になることがある。
- レイヤーの配置: ケミカルバリア層(EVOH)は通常、機械的強度層(PETまたはナイロン)とヒートシール層の間に挟まれ、取り扱いからバリア特性を保護する。
性能目標を前もって設定する:必要な保存期間についてOTRとMVTRの数値を指定し、加速老化試験で検証する。
機械的特性に基づく材料選択
耐パンク性、シール性、印刷適性を考慮して基材を選ぶ。考慮する:
- PET 寸法安定性と印刷品質のために。
- ナイロン 耐穿刺性および耐摩耗性(鋭利な粒子状製品に有効)。
- PE/PP 密封性と単一素材のリサイクル可能なパスのために。
- 添加物/トリートメント: 印刷接着のためのコロナ処理、粉体の帯電防止コーティング、ハンドリングのための滑り止め剤。
厚さのバランス:フィルムを厚くすると保護性能は向上するが、コストと重量が増加する。一様に厚いウェブを使用するのではなく、的を絞った補強(厚いベース層)を使用する。
製造プロセスとラインの統合
平底パウチのデザインは、成形装置や充填装置とマッチしていなければならない:
- ウェブハンドリングと登録: タイトなコントロールにより、ガセットのズレや見当はずれの印刷を防ぐことができる。
- 襟の形状を形成する: カラーが悪いと、シワや折り目のズレが生じる。
- 充填システム: 容積式カップ、オーガー、または計量フィラーは、それぞれ異なるダストと流出挙動を持つため、カラーとトップシールの設計ではこれを考慮する。
- インラインのアドオン: ジッパーの塗布とスパウトの取り付けは、同期したステーションを必要とし、しばしばライン速度を低下させる。
主要パラメータ(ウェブ張力、シール温度、充填重量)を監視し、トレーサビリティのためにログに記録します。
品質管理、賞味期限の相互作用、試験
QCは材料、工程、完成したパウチをカバーしなければならない:
- 着信チェック バリアCOA、厚さ、視覚的欠陥。
- 進行中: ピール強度の抜き取り検査、重量監査、目視登録検査。
- 完成品テスト: OTR/MVTRの検証、加速保存可能期間(例:40℃/75%RH)、耐パンク性、実際の流通シミュレーション。
また、製品とパッケージの相互作用も評価する:油の移行、水分の取り込み、風味の移行は、長期的な製品品質に影響する。
クイック導入チェックリスト
- 充填タイプ、粒子径、油分含有量、目標保存期間など、製品の仕様を定義する。
- OTR/MVTR目標を設定し、候補ラミネートを特定する。
- プロトタイプ 平底袋構造 ジオメトリーと、目標充填重量でのスタンディング挙動をテストする。
- シールパラメータを検証し、ピール/バーストテストを実施する。
- 意図した充填ラインでパイロット運転を行い、加速貯蔵寿命試験を実施する。
- アートワーク、公差、QCサンプリング計画を最終決定する。
結論
について 平底ポーチ は、形状、シール材、バリア材を単独で評価するのではなく、システム全体の構成要素として扱うと効果的です。フラットボトムパウチの形状、素材、そして性能特性に関する製造上の吟味を総合的に見ることで、優れたスタンディング能力を持つパウチ、優れた機能を持つシール、そして流通と使用全体を通して包装された商品の保護に関する性能を持つパウチが生まれる。
GQ PACKについて,GQ PACKはプロの軟包装メーカーとして、独立した設計チームと自動化された生産ラインを持っており、水ボトルラベル、シュリンクスリーブラベル、軟包装袋などの種類をカバーし、高性能のカスタマイズされた軟包装製品を提供し続けています,GQ PACK軟包装メーカーについて,GQ PACKは2008年に中国広東省で設立されました。我々は豊富な経験と特許技術を持つ軟包装メーカーです。製品は、カスタム水ボトルラベル、シュリンクスリーブラベル、スパウトポーチ、スタンドアップポーチなどが含まれ、飲料、食品、日用品、ペット用品業界で広く使用されています。先進的な高速印刷機とラミネート機を装備した16の生産ラインを持ち、経験豊富な技術チームにサポートされており、高品質でカスタマイズされたパッケージングソリューションを提供しています。,コアバリュー,品質,革新,持続可能性,効率性,企業ビジョン,グローバルな顧客のための信頼されるフレキシブルなパッケージングパートナーになる,顧客コミットメント,効率的な、専門的かつ高性能なパッケージングソリューションを提供する,高速10色グラビア印刷ワークショップ,私たちの高速10色グラビア印刷ワークショップは、高度な印刷設備を装備し、高精度自動印刷システムを採用し、極端な細部と豊かな色の完璧なプレゼンテーションを達成することができます。GQ-PACKの無溶剤ラミネーション工場では、有害な溶剤を使用しない無溶剤ラミネーションプロセスを採用しています、PACKの無溶剤ラミネートワークショップは、熱と圧力を利用して複数のフィルム層を接着する高度なラミネート技術を備えており、耐久性、強度、柔軟性に優れたパッケージを作成することができます。PACKはプロフェッショナルなUV硬化システムと熱硬化システムを備えており、硬化したフレキシブルパッケージングが優れた耐摩耗性と防水性を持つことを保証します。検査ワークショップ,私たちは最新の自動検査システムを使用し、包装されたすべての製品がお客様に届く前に最高の品質基準を満たしていることを確認しています。さらに、包装の耐久性、シールの完全性、バリア性を確認するために、包装のすべてのバッチで極端なテストを実行します。 高速スリッター工場,私たちの高速スリッター工場は、迅速かつきれいにフレキシブルフィルム、ラミネート、特殊フィルムを含むさまざまな材料を処理し、均一なロールサイズを提供し、卓越した速度と精度で大量生産の需要を満たす、軟包装製袋工場,当社の軟包装製袋工場は、品質、スピード、精度を重視し、専門的な裁断、製袋、シール設備を備えており、各バッチの製品が正確な寸法、確実なシール、きちんとした外観を持つことを保証します、+ M²,工場面積,生産ライン,技術スタッフ,百万人,年間生産量,GQ Packはフレキシブル包装ソリューションを提供します:,飲料,食品,日用品,パーソナルケア,ペット用品,特殊カートン,農業,技術的なアプリケーション,なぜ私たちを選ぶ,私たちの工場の表示,国際認証,GQ Packは、ISO 9001、FDA、LFGB、CE、RoHS認証などを含むフレキシブル包装の分野で多くの認証を得ています。私たちは、製品の品質とユーザーエクスペリエンスを重視し、常に生産プロセスにおける持続可能な開発を堅持しています。,私たちのビジョン,包装はカラフルで、創造的で、強力です。,私たちは、各フレキシブルパッケージを作るとき、我々は製品だけでなく、無限の可能性を見ています。,私たちは能力を持っており、我々は常にこのようなものです。,私たちが作成するフレキシブルパッケージは単なる容器ではありません、それはブランドの物語のキャリアであり、製品の品質の送信機です。,どのような産業であっても、私たちのパッケージは、製品が市場とシームレスに接続し、信頼と価値を伝えることができます。

GQ PACK は カスタムフレキシブルパッケージングメーカー 数十年にわたりフレキシブルパッケージング業界に専念してきました。提供できるサービス 卸売フラットボトムポーチ 供給と仕立て カスタムフラットボトムパウチソリューション.印刷、ラミネート加工、コンバーティングを監督する自社生産施設により、あらゆる規模のブランドに対し、一貫した品質、予測可能なリードタイム、柔軟性の高いカスタマイズを提供します。
よくあるご質問
Q: なぜ袋の底にしわが寄るのですか?
A: 通常、フォーミング・カラーのセットアップまたはウェブ・テンションが正しくありません。張力を再調整し、フォーミングカラーをチェックしてください。
Q: シールが弱かったり、漏れたりする原因は何ですか?
A: シール爪が汚れているか、摩耗して いるか、または温度・圧力が低い。ジョーを清掃し、シーリングパラメー タを少し上げる。
Q: ガセットはなぜずれるのですか?
A: レジストレーション不良または成形部品の磨耗。ガイドを再調整し、成形部品を点検/交換する。
Q: 何がラミネートの剥離を引き起こすのですか?
A: フィルムのロットの不適合または欠陥。ロールを分離し、ラミネーション仕様/COAをサプライヤに確認してください。
Q:全体的に欠陥の再発を防ぐには?
A: SPCを使用して主要なパラメーターを監視し、8D根本原因分析を適用して恒久的な是正措置をとる。







